What Is A URL?
Uniform Resource Locator (URL), also called Links, is human-readable text that helps users or the search engines to locate your Web page online.
There are two different types of url: Absolute URLs and Relative URLs.
While an absolute URL includes the full address of the website it refers to, Relative URLs display the location of the file in relation to your present position on the website.
How much does URL matter for SEO? After choosing a good url domain, the effectiveness of your SEO strategy depends on how you structure your website url.
What is URL Structure?
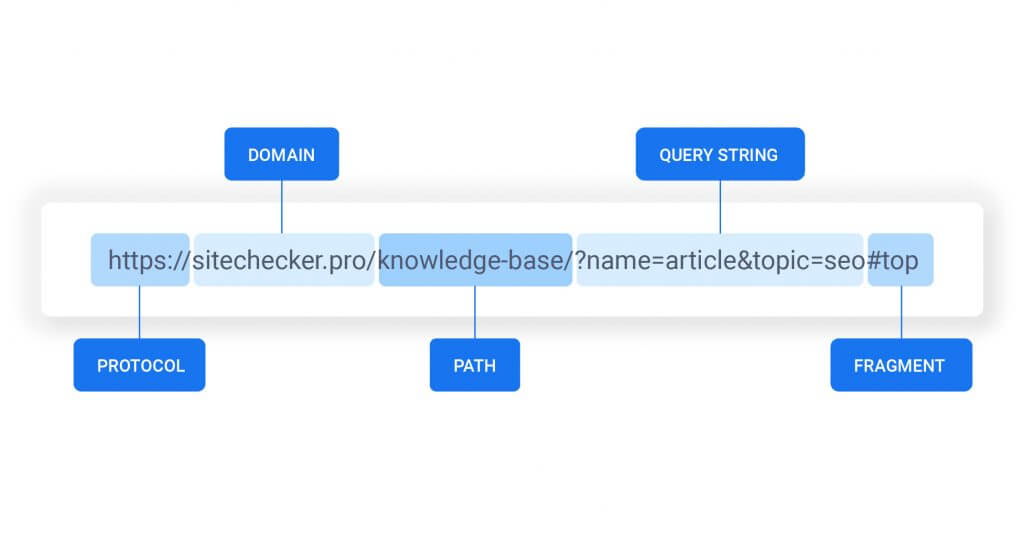
Url structure is the anatomy of a url that includes every part of the url. E.g scheme, domain, and Subdirectory.
The specific requirements of a website determine its URL structure.
An international website’s URL, for instance, is likely to be set up for many locales or languages. A blog URL may be different from an e commerce URL or a business URL. The URL structure of a website for education will probably be different from that of a social network.
While too many care less how their URLs are structured, they go a long way to make for a good url rating.
A thorough understanding of the parts can help you to further optimise your URLs for a flawless SEO game.
What are the Parts of a URL?
Scheme
The scheme identifies the protocol that a web server should use when accessing a page on your website.
Most websites now use HTTPS — which stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure — because it instructs your web browser to encrypt any data you input on the page.
Other schemes may include the ftp://, which is a common protocol for transmitting data between a client and server on a network of computers. Or, the mailto://, which opens your default email service provider to assist you in drafting emails to the email address you supplied in the URL.
Subdomain
A subdomain in a URL identifies the specific webpage of your website that the web browser should display.
For example, https://new.example.com. “new” is a subdomain and in essence the link tells the website that there is more to the website than the homepage.
Second-level Domain
The name of your website is its second-level domain (SLD). It makes visitors more aware that they are on a specific brand’s website.
For instance, everybody who visits “wikipedia.com” knows they are, without the need for more explanation, on the Wikipedia website.
Top-level Domain
The top-level domain (TLD), defines the specific sort of entity a company identifies with on the internet.
For instance, “.com” is meant for commercial companies, hence many business urls use it as their top-level domain.
Similar to “.edu,” which is reserved for educational institutions, many colleges and universities register their websites with “.edu” as their top-level domain.
Subdirectory
A subdirectory, often referred to as a subfolder, makes it easier for users and web crawlers to identify the specific section of a website they are on.
For example, if you have an online store selling phones, computers, and gear, one of the URLs for your website might be “https://shop.example.com/gears”.
Take note that “shop” is the subdomain and “gears” is the subdirectory. This means that the “Gears” page, a subfolder of the “Shop” page, would be presented by this URL. Other subfolders of this page would be for phones and computers.

Why Does URL Structure Matter for SEO?
• Ranking: Search engines employ URLs as a supplemental ranking criterion to assess how relevant a page or resource is to a given search query. While they do take into account the domain’s overall authority, keyword inclusion in a URL can also influence rankings.
When you optimize your URLs for humans, you also make it simpler for search engine bots to crawl and scan your website so that it can show relevant results to users who are conducting searches.
In other words, improved URL structures help Google PageRank (PR). Google uses PageRank to evaluate a web page’s worth and its relevance to a search query.
Although employing a URL with keywords can increase your site’s search ranking, URLs generally have little bearing on how well a page ranks. Therefore, while it’s something to consider, avoid making URLs that are otherwise useless only to have a keyword in them.
• Increased User Experience: Google has recently been changing the link in the snippets area of their search results with site name and breadcrumb path.
When it comes to SEO, a great user experience is the most crucial component.
Use a sensible URL structure with page hierarchies to enhance user experience. Your website will be simpler for people to navigate if the content is intuitively organized.
A good url will still give visitors a good notion of what the destination page is about, this human-readable, semantically accurate URL would also improve their user experience by making it obvious what they may expect when they click the link.
Compare this:
https //www.example.com/books/how-to-win-friends.
With:
https://www.example.con/folders/e4bgt_tbs
The former is most likely to be clicked because the user will perceive clicking the link as relevant to his search. However, the latter might leave the user in doubt.
URL Structure Best Practices
• Use language that people can understand.
Even though URLs can contain ID numbers and codes. Keeping your URLs as short, relevant, captivating, and accurate as you can (a prerequisite to ranking well) the key to making your URLs understandable to consumers and search engines alike.
Defining yet brief URLs are best. A user (and search engine, too!) should be able to predict what to find on the website by merely looking at the URL.
For example, an e-commerce url should look something like this: https://www.example.com/categpry/subcategory.
The product url can also look like this: https://www.example.com/category/subcategory/Product
This makes it easier for users and search engines to easily predict how relevant your web pages will be to the search.
• Don’t use stop words or special characters.
Your rankings may be affected by URLs that contain special characters like ampersands, asterisks, and exclamation marks, stop words like “the” and “an,” because only a maximum of 70 URL characters can ever be displayed, it is best practise to leave out terms that don’t add anything.
The use of url parameters can ruin your SEO strategy if it is not properly handled. You should definitely avoid using special characters because they could lead to indexing problems.
• Use hyphens instead of underscores in your URLs.
While Google will not identify an underscore in your URL, it will recognise hyphens as word separators.
This indicates that utilizing hyphens makes it considerably simpler for Google to get keywords from urls. For instance, a URL containing “my shop” would be read as “myshop” rather as “my shop.”
• Avoid using URL parameters as much as you can because they can lead to tracking problems and duplicate content difficulties. If parameters are necessary (UTM codes, for example), utilize them sparingly.
• Keep a consistent URL Structure.
There are myths around the length of a url and its impact on ranking. However, using one word URLS or long URLS makes no difference to ranking.
“It is best to keep the URL length under 1000 characters” says Google’s John Muller in an interview
The days of trying to outsmart the algorithm are gone. It is clear that a properly optimized URL structure is a plus to your SEO Strategy.